It’s not new for a country that has recently achieved its independence to plunge into chaotic bloody civil war, or initiate policies that are hostile to the country it separated from. A good and recent example of this is South Sudan, which became independent from Sudan in 2011. No sooner than South Sudan left the Sudanese Republic than disputes began to emerge with Sudan over crucial natural gas supplies, prices and pipelines. Worst at all, the country plunged into bloody civil war that is still raging today, where civilians are get killed along ethnic and religious lines. The various new militias are raping, killing and maiming at will.
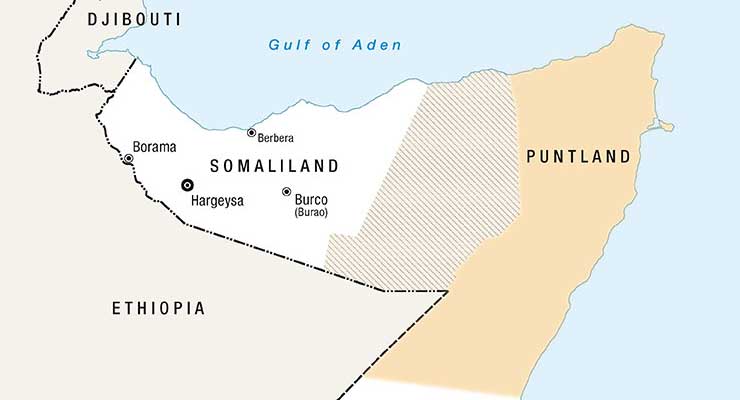
This scenario can unfortunately be compared to Somaliland which if recognized as an independent nation could have detrimental effects on the itself and the wider region. First of all, Somaliland remains an unstable and unrecognized breakaway region divided along clan-lines. Half of the population support and say they are part of Somalia while the other half are divided on the issue, only a minority are hardcore secessionist. Luckily for Somaliland, no nation came to recognize it. The reason being is largely to preserve the territorial integrity of Somalia and a fear that this autonomous region might descend into chaos along clan lines.
The Relevance to Somaliland
Since the unilateral declaration of independence from Somalia, Somaliland has achieved very little in delivering basic infrastructure. Infrastructure is dilapidated as a lack of educational facilities and water shortages in even the largest cities of Somaliland continue.
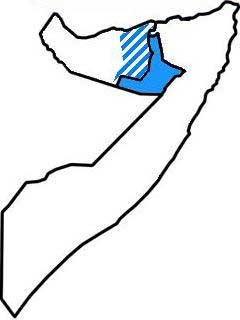
Somaliland is also in constant conflict with Khatumo State which claims the region of Sool, Sanaag. Recently, clashes over a well-holes took place between clans from both entities resulting in high human and material loss on both sides. Some analysts assert that – similar to that of South Sudan – Somaliland will descend into perpetual civil war if the world community recognized it an state.
After 2007, a no war, no peace relationship has reigned over Somaliland and Khatumo State which is allied to the Federal Government of Somalia. However, a new development is likely to change things for the better. The International Community has decided to support the fragile Somali Government by injecting millions of dollars into the capital Mogadishu to enhance its security, boost investment in critical infrastructure like the energy sector and road construction. A reliable working government in Mogadishu would likely evaporate the one clan dream in Somaliland and ensure the territorial integrity of Somalia.
One major difference is that Somaliland unlike South Sudan has no proven oil and natural gas. The regions that contain oil is disputed with Khatumo State, another region like Somaliland that are allied with the Federal Government of Somalia.
Finally, any move to recognize Somaliland as independent from Somalia has serious implications for Ethiopian national security and survival of the Ethiopian state since more than 12 ethnicities in Ethiopia wants to separate from Ethiopia. The precedence set by a move for independence in Somaliland would therefore be a mistake with regional repercussions.
Saeed camir says
The American features Somaliland Op-ed by IRI Board Member
JULY 28, 2010
Somaliland and the March of Freedom
The American
By Ambassador Richard S. Williamson
The most recent entry in freedom’s ledger was written in late June in an unlikely corner of East Africa.
While the voice of President Obama has grown quiet in championing the spread of democracy, the fire for freedom still burns bright in the hearts and minds of people around the world.
Freedom and democracy are difficult to achieve and not inevitable. Nonetheless, history continues to witness freedom flower even in inhospitable soil when patriots cherish personal liberty and are persistent in its pursuit. The most recent entry in freedom’s ledger was written in late June in an unlikely corner of East Africa.
Somaliland is desperately poor, Muslim, and nomadic. It has few natural resources, and its limited exports are primarily livestock and fish shipped to Yemen. The international community has not recognized Somaliland and provides it little support. When their brutal war with Somalia ended in 1991, the country had been ravaged.
With the horrors of war still fresh, Somalilanders cherish peace. The violent failed state of Somalia to their south reminds them what they must not allow to infect their own society. And they have hope. Over lunch, University of Hargeisa President Dr. Hussein Bullan said: “It is the Somaliland way: No wells will be dug for them. No rescuers are coming for them. At the university we teach the students that no wells will be dug for them, but you are the rescuers.”
The violent failed state of Somalia to their south reminds them what they must not allow to infect their own society.
In 2001, Somalilanders held a constitutional referendum, opening the door for democracy. From 2002 to 2005, there were three elections—for local offices, the presidency, and parliament. All were deemed acceptable. The 2003 presidential election was decided by a mere 80 votes and the defeated candidate accepted the result, and the 2005 parliamentary elections produced an opposition majority. So far, so good.
But this year’s presidential election, just completed, provided ample evidence of the challenges a nascent democracy faces. The vote was originally scheduled for 2008 but was repeatedly delayed as tensions rose across the country and the nation’s democratic institutions were severely stressed. Leading up to the election, Somalia Islamist Al-Shabab, which has links to al-Qaeda, threatened to disrupt the vote. All this contributed to an atmosphere of uncertainty leading up to this election.
But the people would not be denied.
I was in Hargeisa for election day as head of the International Republican Institute’s Election Observer Mission. What I witnessed inspired me and belied the cynics who would deny freedom’s march and would dim America’s tradition as a “shining city on the hill” for human rights and democracy. Advancing these values is our opportunity and our responsibility.
On election day I arrived at a polling station at Waa Kiro School in Hargeisa at 6:30 a.m., 30 minutes before voting was to begin. More than 300 people were already waiting to vote. Betra, a woman in her thirties with seven children, was first in line. I asked her when she had shown up. She told me 2 a.m. “Why?” I asked. “This is an important day for me and my children,” she replied. “The election means good things will happen.”
When I asked him why he was waiting in line to vote, Abdirahman, a young man, echoed the sentiments of many American voters. He said simply, “I want change.”
I met Amina at a polling station at the Imamushashifi School in a deeply impoverished section of Hargeisa. She’s 29 years old with five children, and the youngest, a five-month-old infant, was strapped to her back. She had arrived to vote at 5 a.m., and at 9 a.m. was still waiting for her turn. With a broad smile she told me, “Life is good in Somaliland, and with this election it will get better 100 percent.”
This year’s presidential election, just completed, provided ample evidence of the challenges a nascent democracy faces.
It was not just hope nor youthful enthusiasm that brought hundreds of thousands of Somalilanders to the polls. There was a deeper understanding of democracy’s promise. At the Puoostu Total School polling site, I met Ibrahim, a 65-year-old man and father of 13 children, who told me he was jailed for three years in Somalia when young on trumped-up charges because he had offended a soldier. Ibrahim observed, “Democracy is very good for Somaliland. If there is democracy every human being will get his rights. From the fighting with Somalia there are mass graves everywhere in Somaliland. They want to kill the people like animals. We are getting stronger. Democracy makes the institutions of government stronger.”
A number of voters told me about the accountability that democracy brings. In a small village with dusty dirt roads about an hour outside Hargeisa, Hussein, a 40-year-old public notary voting late in the afternoon, told me that “the candidates have made promises and they will have to deliver or else.”
In Somaliland, the democratic process is helping to bring in a younger generation of people. And as the democratic process deepens, the hold of the traditional, male-dominated clan leadership weakens.
Like all elections, including our own, there were some irregularities. But it was an orderly, generally peaceful, credible election in which Somalilanders rejected the incumbent ruling party. Ahmed Mohamud Silanyo, the main opposition leader, has been declared the winner. President Dahir Riyale Kahin has accepted defeat. In East Africa that still is a remarkable event. That’s democracy at work.
Berbera is a coastal town in the northwest region of Somaliland where temperatures in the summertime can approach 122 degrees Fahrenheit. Here one of my colleagues met Hinda, a Somalilander who had immigrated to the United States, married an American, and now lives in Minneapolis. Thirty-four years old, she has two sons, ages 13 and 12. She was working as an election observer. She had brought her two sons with her, neither of whom had ever before visited their mother’s homeland. She wanted to bring her children this long way so they could know their culture and see its promise. She is proud of the nascent democracy in her native land. She said she had worked in the 2008 Obama campaign and wants to do the same thing in Somaliland.
Despite President Obama’s lack of enthusiasm for freedom’s march, there are others for whom the fire burns bright, including those whose democratic impulse helped him become leader of the Free World.
Ambassador Richard S. Williamson is a principal at Salisbury Strategies, LLP. He has served as an ambassador and U.S. representative in several capacities to the United Nations, as an assistant secretary of State, and as assistant to the president for intergovernmental affairs in the White House for President Ronald Reagan. In January 2008, he was appointed special envoy to Sudan by President George W. Bush.
Shakir says
We must work together as Somali’s. The civil war has affected everyone-south, north, central. It’s time everyone moved on. Somalia is a small country. We share the same language, culture, ethnicity, and religion. The north consists of 5 provinces and approximately 6 clans and vast majority of them do not want to divide Somalia. The one group who want to divide reason is because Moqadishu is lawless. The same can be said in north (somaliland) where there is a lot of clan tensions-Sool, Sanaag, Awdal provinces. Moqadishu and many parts of Somalia is getting better. So let’s all work together.
Abshir says
dude,that was 2010,6 years have passed.